So, you’re searching for the best hearing aids? That’s no small task. When I bought my first pair (before starting this site), I was struck by how complex the process was. It wasn’t like picking out headphones or even a new dishwasher—the stakes felt high, the terminology was unfamiliar, and the last thing I wanted was to make a mistake I couldn’t undo. That experience ultimately inspired this website—and this guide.
Over the past few years, I've tested more than 100 hearing aids—send good thoughts to my ear canals. I've worked with leading audiologists and manufacturers to break down the technology inside these devices, while also digging into often-overlooked details like app functionality, stability, and physical comfort.

Below, you'll find our ever-evolving answer to one big question: What are the best hearing aids on the market? We’ll walk you through new brands, trusted staples, and how to determine which option fits your needs. Click through each product for an in-depth video review and a detailed breakdown of its features and functionality.
Beyond the product recommendations, we zoom out to cover the hearing aid selection process as a whole—how to understand your hearing test, choose the right style, explore financing options, and more. By the end of this guide, you'll have everything you need to make a confident, informed decision.
Let’s dig in - we got this! 🤝
- Hearing aids range from $400 to $5,000 per pair. The price difference largely depends on whether you work with a local doctor or go for an over-the-counter (OTC) option.
- Start with a hearing test. Take our free online hearing test. It’s a simple way to understand whether OTC hearing aids are a good fit or if you’d benefit from seeing a doctor.
- Hearing aid tech is better than ever. Recent advancements include upgraded Bluetooth features, long-lasting batteries, and AI-powered sound processing. It’s an exciting time to shop for hearing aids!
- The best devices come from trusted manufacturers. Our favorite options on the market (regardless of care model) come from manufacturers who have been in the hearing aid space for decades (WSA, Sonova, GN)
- 50+ hearing aid brands reviewed and rated by our team of hearing aid wearers and audiologists
- 200+ hours each month spent researching brands and care options
- 2,000,000 people shopped on Soundly in 2024
- 100% independently owned and operated
Read more about our company, services and process here.
Featured in this article
How We Chose The Brands On This Guide
Every month, we test and review dozens of hearing aids to create a balanced guide for every need. I’ve personally worn 50+ devices, testing for comfort and performance in real-life settings (read more about me here). Our lead audiologist, Amy Sarow AuD, CCC-A runs extensive technical tests in our studio.
We also learn from thousands of Soundly customers by analyzing return rates, technical issues, and general feedback across the products we carry. That input, combined with our own testing, helps shape the recommendations we make.
Ultimately our goal is to find the best product for you - whatever your situation is. Got feedback on the list? Email us at [email protected].
Here’s what we look for in great hearing aids:
- Reputable brands: Every brand we feature is serious about hearing health, with proven experience in manufacturing, warranties, and long-term care—qualities that matter over time.
- Sound quality: We test products in a variety of settings, including challenging environments with background noise. Sound quality is crucial, and we factor that heavily into our analysis.
- Physical comfort: Even the best sound quality won’t matter if the device isn’t comfortable to wear. We’ve selected hearing aids that offer both comfort and performance.
- Various price points: Finding the "best" hearing aid means something different for everyone, so we’ve included options across a range of price points.
In this guide, we’ll cover two main categories of hearing aids:
- Over-the-Counter (OTC) options, which can be purchased without a prescription and are designed for self-fitting at home.
- Prescription hearing aids, which are typically fit and programmed by a licensed professional at a local clinic.

Product Group 1 - Over-The-Counter (OTC) Hearing Aids
Appropriate for mild-moderate hearing loss.
This first group of hearing aids gives you control over the tuning process and tends to be the most affordable. Using a smartphone app, you can customize these devices to match your hearing loss. This model not only saves money, but studies from The Journal of the American Medical Association have shown that OTC hearing aids deliver clinical outcomes nearly identical to prescription devices.
These are our favorite over-the-counter hearing aids. 👇
Sennheiser All Day Clear
- Our favorite OTC hearing aids for under $1,000
- Manufactured by the largest hearing aid maker in the world
- Compatible with iPhone and Android devices
Sennheiser All Day Clear is our top-selling and best-rated OTC hearing aid at Soundly.com. We’ve tested this product extensively—in the audiology test box, in real-world noisy environments, and through thousands of Soundly customer experiences in 2025.
Soundly offers a complimentary setup call with every purchase — a helpful perk for customers and a valuable way for us to hear firsthand which products are performing best.
At-Home Delivery

Sennheiser All Day Clear is made by Sonova, the world’s leading hearing aid manufacturer. Unlike traditional in-clinic devices that average around $5,000 a pair, All Day Clear ships directly to your home (Soundly offers free 2-day shipping) and lists for $999 per pair.
Rechargeable with Bluetooth
These hearing aids deliver 18–20 hours of battery life on a single charge and offer reliable call and music streaming for both iPhone and Android users. Thanks to Sonova’s Bluetooth Classic connection, pairing is easier than most OTC devices—especially for Android users.
App Programming

As a self-fitting product, All Day Clear uses a smartphone app to adjust the hearing aids to your specific hearing loss. The app isn’t the most feature-rich on the market, but in our testing (and from what we hear from customers), it’s the easiest to set up and navigate.
Sound Quality
Likely your biggest question: how do they sound? In short—excellent. You can hear Sonova’s signature processing in these devices. They handle sudden sounds, wind, feedback, and background noise in a way we’d consider market-leading for OTC self-fitting hearing aids.
Notes & Watchouts
- Best suited for mild-to-moderate hearing loss. If your loss is more significant or complex, in-clinic care is still the right move. Take our hearing test to better understand your loss.
- The charger must be plugged into the wall while in use. A separate power pack is available if you want mobile charging.
Bottom line: Sennheiser All Day Clear sits at the top of our list for self-fitting OTC hearing aids. It delivers great sound, simple control, and strong value from a world-class manufacturer.
You can purchase Sennheiser All Day Clear hearing aids directly through Soundly for $999 per pair and access all of our care and services.
We recommend taking our hearing test before purchasing. Our team can review your results and offer a second opinion if needed.
Once you’re ready, you can place your order on the website or over the phone.
- Sennheiser orders come with 100-day risk-free returns — exclusively on Soundly.
- Your hearing aids ship 2nd Day Air to your home.
- Upon arrival, you’ll receive setup instructions and use the smartphone app to customize your hearing aids.
- Sennheiser includes starter domes in the box; you can purchase alternate sizes and styles through Soundly.
- Every order includes a complimentary setup session with one of our hearing professionals.
- We offer MSRP pricing and deals and will price-match any other official retailer offering the same product and terms.
- Soundly provides 45-day price-drop protection—if the price drops within 45 days, contact us and we’ll refund the difference.
Here's what Dr. Amy Sarow, Audiology Lead at Soundly, had to say about the Sennheiser All Day Clear:
What is your experience supporting customers directly with this product. What comes up a lot?
Customers often ask about how to adjust their devices to match or closely align with their audiogram. While OTC devices use ‘presets’ - if they have a mild to moderate high frequency loss, we can usually come close to what is appropriate for their needs.
The Sound Profile uses three categories during the setup: volume, clarity, and balance. We generally perceive volume in the low frequencies, most people have normal hearing to mild hearing loss in that region, so the preset default of 3 is usually fine.
The clarity setting is the amount of high frequency amplification. The default here is also 3, which is appropriate for a mild loss and for a moderate loss a high number is more appropriate (i.e., a 5 or 6). The balance setting allows the user to adjust volume for right and left separately.
Customers often ask how to keep the adjustments when they ‘split’ the volume on the main app screen, but this setting will revert back to the middle after the hearing aids are placed in the charger and taken out again the next day.
Compared with other hearing aids at a similar price, where does Sennheiser All Day Clear stand out, and where does it fall short?
Compared to other products at the same price point, Sennheiser All Day Clear shares the processing of its prescription counterparts (Unitron and Phonak).
The sound processing feels smoother and more sophisticated than some other options in this pricepoint or lower.
The ADC also does an excellent job of feedback suppression, with some other similar OTC products more prone to feedback in the ear.
However, the ADC app falls a bit short compared to some of the other OTC apps. For example, no direct controls in the app for background noise suppression, ability to directly select hearing aid programs.
The app feels a bit more simplistic than some comparable OTC brand apps.
Who is this product best for?
This product is best for those who have mild to moderate hearing loss and works particularly well for a sloping hearing loss configuration.
For those with normal hearing in the low frequencies, they may experience some static or white noise sound, but this can be reduced by adjusting the ‘mid’ category down on the equalizer.
Additionally, this product works well for those who like to stream audio via Bluetooth, works better than other products for those who like to listen to music, and is a great option for those who prefer an app that keeps things simple.
It’s not always the best choice for glasses wearers (though still possible) or those with very petite ears.
- Premium Sonova-built technology for less than prescription channels
- Bluetooth streaming and hands-free calls (Android and iPhone)
- Comfortable all-day form factor
- Charger must be plugged in while charging
- Requires a smartphone for programming
- All-Day Clear is an OTC product appropriate for mild-moderate hearing loss levels
- If you have more significant hearing loss you might consider local or Telehealth care. Read more about prescription Vs. OTC hearing aids here
- Available for purchase online via Soundly
- Does not require a prescription from a doctor
- Customize your hearing aids with the Sennheiser All-Day Clear app
- Soundly customers get a complimentary guided setup session
- Sennheiser offers impressive underlying background noise management technology
- We found this product performed at a similar level to top prescription brands
- Comfortable receiver-in-canal style is great for all day wear
- Sits behind the ear with a receiver (speaker) that reaches into the ear canal
- The form factor of Sennheiser All-Day Clear is comparable to leading prescription hearing aids like Phonak Lumity
- Available in a dual-tone black and silver
- Choose between slim and non-slim versions (we recommend the non-slim option for most people)
- Sennheiser All-Day Clear comes with rechargeable batteries
- 16 hours of wear on a single charge
- Recharge case must be plugged into the wall while in use
- All-Day Clear streams to all devices including iPhone and Android
- All Day Clear allows hands free phone calls on both iPhone and Android
- Streaming quality is similar to the top prescription products on the market
- All-Day Clear is reasonably easy to handle but does require the wearer to place the hearing aid behind their ear and insert the receiver into the ear (consistent across all behind-the-ear styles)
- The All-Day Clear recharge case has ports that must be in contact for charging. This type of charger is more difficult than premium conduction chargers which do not require ports to be touching
- Sennheiser All-Day Clear hearing aids have an IP68 rating
- These devices can be submerged in up to one meter of water for 30 minutes without damage
- The Sennheiser All-Day Clear app enables setup and customization of your hearing aids
- The smartphone app allows on-the-go volume and sound quality adjustments
- The All-Day Clear app has a music and automatic program but does not offer Tinnitus masking, program creation or other advanced features
Eargo 8
- Disruptive leader in hearing health, known for sleek, invisible design.
- Rechargeable with a patented ear tip that allows ears to breathe.
- Eargo 8 adapts to your environment automatically throughout the day.
- Budget models (Eargo SE and Eargo LINK) offer lower prices and alternate features.
Eargo has long set the standard for invisible-style design in the hearing aid industry. Their compact devices, along with an intuitive app and thoughtful packaging, make Eargo a standout choice for early adopters. Here’s why we picked it:
- Invisible Design: The Eargo 8 is one of the smallest rechargeable hearing aids on the market, rivaled only by the Sony CRE-C20.
- Reduced Occlusion: Eargo’s patented “floating” ear tip design sits comfortably in the ear without causing occlusion, a common issue for in-ear hearing aid users.
- User-Friendly App: The Eargo app is easy to navigate, and it allows audiologists to remotely adjust your devices as needed, though most adjustments can be managed directly in the app.
Eargo has received numerous customer reviews, reflecting a generally positive reception.
Overall
Customers frequently commend Eargo for its discreet design, sound quality, and responsive customer service. Many users highlight the significant improvement in their hearing experience and the comfort of the devices.
Positives
- Discreet Design: "The Eargo hearing aids are virtually invisible, and no one can tell I'm wearing them." — James D.
- Sound Quality: "The clarity of sound is remarkable; I can hear conversations clearly even in noisy environments." — Charlie B.
- Customer Service: "Eargo's support team was incredibly helpful and guided me through the setup process with ease." — Rowdy G.
Complaints
While the majority of feedback is positive, some customers have reported issues with device durability and the need for adjustments. However, these concerns are relatively infrequent compared to the overall satisfaction expressed by users.
For a comprehensive view of customer experiences, you can visit Eargo's review page.
- Eargo is a tiny, rechargeable device that sits entirely inside the ear
- Eargo uses a unique design that prevents occlusion
- Eargo is self-fit using an app but offers remote support
- Only appropriate for those with mild to moderate hearing loss
- Requires some tinkering to fine tune the product
- Eargo is not Bluetooth enabled due to the tiny size
- Eargo 8 hearing aids are sold over the counter and are appropriate for those with mild-moderate hearing loss
- If you have more significant hearing loss it is recommended that you access professional care through Telehealth or local care
- Available for purchase online or at retail stores like Verizon Victra and Best Buy
- Does not require a prescription from a doctor
- Customize your hearing aids with an onboard hearing test and app-controls
- Eargo has well-developed background noise management algorithms
- Smart Sound Adjust automatically adapts to your environment and focuses on voices
- Eargo sits inside of the ear and is one of the most comfortable in-ear options on the market
- Eargo creates less occlusion than many in-the-ear options
- Our team finds all in-the-ear models slightly less comfortable than RIC hearing aids
- Sit inside the ear
- Only available in one completely-in-canal size (nearly invisible in many ears)
- Only available in black
- Eargo hearing aids are rechargeable
- 16 hours of battery life on a single charge
- Each pair of hearing aids comes with a small and portable recharge case that carries 14 additional charges
- Eargo 8 does not offer Bluetooth streaming
- Eargo 8 is small but comes with rechargeable batteries which prevents difficult battery changes
- Eargo's devices include a pull-tab that makes it easier to place and remove the devices in your ears
- Eargo 8 hearing aids have an IP68 rating, meaning they can be submerged in up to one meter of water for 30 minutes without damage.
- Eargo 8 pairs with a smartphone app that includes an onboard hearing test and manual controls for programs, volume, and sound quality.
- You can also adjust volume and switch programs without the app by simply double-tapping your ear.
Nuance Audio Glasses
- Glasses and hearing aids combined
- From the maker of Ray-Ban
- Easy-to-use smartphone app
- Available with multiple style, lenses and colors
Nuance Audio Glasses are one of the most exciting new entries into the hearing aid space.
- Hearing Aids + Glasses: The product combines market-leading eyewear design with a fully functional, open-ear hearing aid.
- Directional Mics: Onboard microphones detect the direction you're facing and deliver real-time amplification of voices directly into your ears.
- Open Ears: Importantly, the glasses don’t go in or over your ear canals, offering both a discreet appearance and a more comfortable, open-ear listening experience.
Nuance is a great option for those with mild-moderate hearing loss or anyone who prefers not to wear traditional hearing aids. The product is available through Soundly here and comes with our full suite of care and support.
Customer feedback on Nuance Glasses has been largely positive, with many users highlighting the open-ear speaker design as comfortable and easy to get used to.
Several people note that the glasses provide clear audio in situations where they would otherwise struggle, making everyday conversations and activities more accessible.
Soundly customers also appreciate the discreet, invisible nature of the device, along with the added convenience of pairing the glasses with prescription or transition lenses.
- Sleek, glasses-style form factor — no in-ear components
- Transitions® lenses included (gray or emerald tint depending on frame color)
- Compatible with prescription lenses via your local optometrist
- Built-in speakers and microphones for discreet hearing support
- No music or media streaming capability
- Battery lasts 8–10 hours — may require midday charging
- Not as powerful as traditional in-ear hearing aids
- Nuance Audio hearing glasses are sold over the counter and are appropriate for those with mild-moderate hearing loss
- If you have more significant hearing loss it is recommended that you access professional care through Telehealth or local care
- Available for purchase here Soundly.com with a complimentary guided setup service
- Does not require a prescription from a doctor
- Customize your hearing glasses using a smartphone app
- Swap your transition lenses for prescription lenses at a local optometrist (prescription lenses not included with purchase)
- Nuance Audio Glasses perform well in background noise (especially in front of you)
- Nuance Audio Glasses leave your ear canals open which can help promote natural awareness
- Nuance Audio Glasses are very comfortable for all day wear due to their open ear design
- Amplification comes through an open speaker placed above the ear canal
- Nuance Audio is the only FDA-cleared pair of hearing glasses on the market at this time
- Nuance Audio Glasses are charged using a charge pad and USBC charger
- Each charge give the user 8-10 hours of wear time (depending on background noise)
- Nuance Audio Glasses do not offer Bluetooth streaming
- Nuance Audio Glasses are among the easiest hearing devices to manage
- No placement of small pieces inside the ear necessary
- Easy charge-pad with bright light to indicate charging
- Protected from sweat, light rain and dust
- Nuance Audio glasses pair with a smartphone app for easy volume control, program updates, and initial calibration
Elehear Beyond
- Our favorite OTC hearing aids for under $500
- Compatible with iPhone and Android devices
- Bluetooth streaming and rechargeable
Here’s why we picked Elehear Beyond:
- Sound Clarity: Elehear Beyond’s noise reduction effectively separates speech from background sounds, providing clear listening in a variety of environments.
- Simple Bluetooth Streaming: Elehear Beyond connects directly through Bluetooth settings, similar to pairing regular headphones. It supports music and calls without requiring extra accessibility setup steps.
- Battery Life: The charging case provides up to 20 hours of use after a 90-minute charge, making it convenient for all-day wear without needing frequent recharges.
- Customizable Sound Settings: Through the Elehear app, users can adjust bass, treble, and volume to match their personal preferences, offering more control than pre-set options in higher-end models.
- Affordable Choice: Priced at $399 per pair, Elehear Beyond is an accessible option in the OTC market, with essential features suited for those who prefer handling adjustments independently.
- "These are amazing for the price! I bought them as a backup to my expensive prescription ones and I use them more often than the originals. The price is amazing for what you get. One suggestion is that there should be sport guards for them to protect from loss"
- "Good hearing aids for the price. They’re effective, but I’ve had some minor issues with background noise in crowded areas. Nothing major, but something to note"
- "I've had the Beyond hearing aids for a few weeks now. They work well, but I’m still getting used to adjusting the settings. Overall, a solid product, but a bit of a learning curve."
- "Thanks to customer support.My hearing aids arrived damaged, customer support was able to replace it in just one day"
- "Comfortable for All-Day WearI can wear these all day without any discomfort. They’re light and fit snugly in my ears. A great fit for daily use."
- "I can hear much better with theseI can hear much better with these, but they sometimes feel a little loose after wearing them for a few hours. Other than that, I’m happy with the sound quality."
- "Finally I can listen to musicI love bluetooth feature, listening my favorite songs directly to my hearing aids feels amazing!!!"
- Robust features for a very affordable price
- Bluetooth streaming (iPhone and Android)
- Tinnitus masking features
- Requires some tech savvy
- Newer company
- Slightly less advanced sound (although impressive for the price)
- Elehear Beyond is an OTC product appropriate for mild-moderate hearing loss levels
- If you have more significant hearing loss you might consider local or Telehealth care. Read more about prescription Vs. OTC hearing aids here
- Available for purchase online or at retail stores
- Does not require a prescription from a doctor
- Customize your hearing aids through dials and controls inside a smartphone app
- Elehear Beyond has the best sound quality we've seen at products under $500
- Comfortable receiver-in-canal style is great for all day wear
- Sits behind the ear with a receiver (speaker) that reaches into the ear canal
- The form factor of Elehear Beyond is comparable to leading prescription hearing aids
- Only available in silver
- Elehear Beyond comes with rechargeable batteries and a portable recharge case
- 20 hours of wear on a single charge
- New recharge case carries an additional 80 hours of portable charge (without being plugged in)
- Elehear Beyond is compatible with iPhone and Android Devices
- Bluetooth connection is managed through the settings app
- Elehear Beyond is reasonably easy to handle but does require the wearer to place the hearing aid behind their ear and insert the receiver into the ear (consistent across all behind-the-ear styles)
- Elehear Beyond has an IPX5 raing
- In practical terms, an IPX5-rated device can handle splashes, rain, and some exposure to water but is not fully waterproof
- Adjust volume, sound quality and background noise
- Elehear Beyond comes with built-in tinnitus management features

Product Group 2 - Prescription Hearing Aids
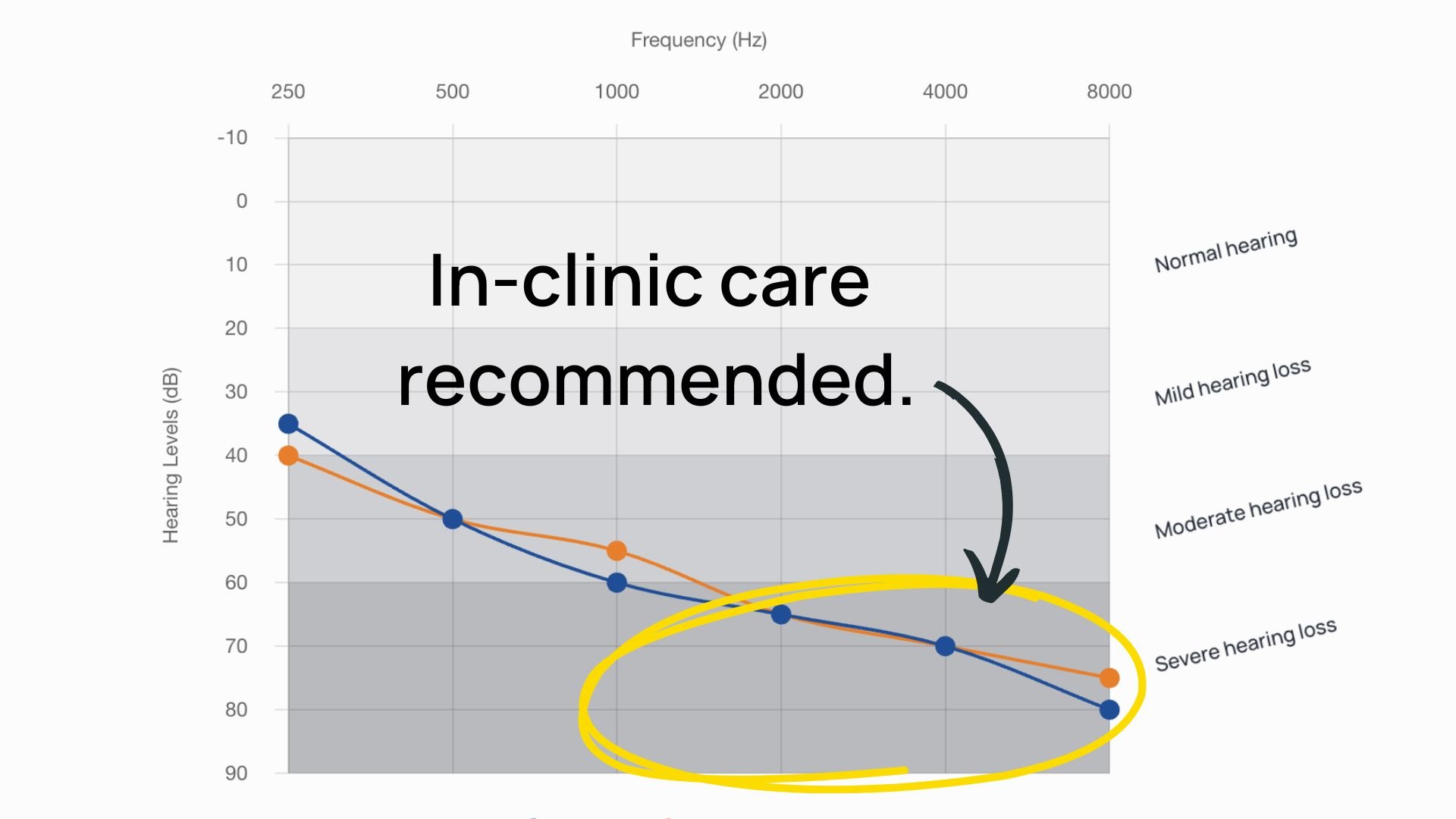
Appropriate for mild-profound hearing loss.
This group of hearing aids is prescribed by local audiologists. They tend to be on the higher end of the price range, costing between $3,000 and $8,000 per pair, and offer top-tier technology.
Nearly all locally prescribed hearing aids are produced by a handful of major brands, known as the "Big 5." These companies invest millions in research and development, often leading the industry in innovation and technology.
While there are some style and philosophy differences between brands, they generally offer the same advanced features and similar price points.
These are our favorite prescription products.
Signia Charge&Go
- Excellent all-around sound processing—one of our top picks
- 39-hour battery life on a single charge
- Compact design: one of the smallest receiver-in-canal (RIC) devices available
- Custom-programmed by an audiologist at your local clinic
Signia Charge&Go is a standout for those seeking a well-rounded prescription hearing aid that combines advanced features, sleek design, and extended battery life. Here’s why we love it:
- Long Battery Life: With up to 39 hours of power (34 hours with streaming), it’s perfect for reliable, all-day use without constant recharging.
- Speech Clarity: Multi-beamforming technology sharpens speech even in noisy environments, helping users focus on conversations with ease.
- Advanced Features: Includes Own Voice Processing (OVP) and Bluetooth LE Audio for smooth streaming from both iOS and Android devices, enhancing audio quality.
- Comprehensive App Support: The Signia smartphone app offers fitness tracking, remote care (after the first appointment), and Signia Assistant, adding customization and convenience.
Customer reviews for Signia Pure Charge&Go are generally positive with nearly all customers celebrating crisp and clear sound. Some customers even report improvements in tinnitus using Signia's in-app tinnitus features. Like all hearing aids, some users find that adjustment to hearing more sound is a process. See more reviews from our partners at ZipHearing.
- "I can hear again!! No more asking people to repeat what they said, turn up the TV, or be staring blankly because I wasn't sure someone was addressing me. I can hear the water that I accidentally left running outside (old pipes in an old house). It's wonderful!!" - Mary
- "I LOVE my new Signia Pure Chareg&Go 5 IX hearing aids. I'm 81 and these are my first so I wondered if I'd have trouble adjusting to the sound or the aids. The answer is neither! The sound is very natural - I'm now hearing highs I haven't heard for decades. From the first day I've been wearing them for 16 hours per day and don't even know they're there." - Jeff
- "The sound quality is very good .Ive had chronic tinnitus for over a year and three months. I use ocean sounds for my therapy , it sounds like you are there. They are discrete and easy to wear . I have reduced my tinnitus by 65 to 70 percent In just about 3 months. Take the step , put in the time and results will follow." - Harly
- "Sound quality is very tinny but from what I've read, that is to be expected. I know my family and friends are happy to not be repeating themselves over and over again. It's very hard to review a product when you have nothing to compare it to." - Colleen
- Among the smallest body size on the market
- Second longest battery with 39 hours per charge
- Excellent in background noise
- Fully customizable with premium sound processing
- Only sold through local clinics at $3,198 - $7,000 a pair
- Does not include a Find My Hearing Aids feature
- Signia Pure Charge&Go is a fully customizable, prescription hearing aid appropriate for mild-severe hearing loss
- If you have severe hearing loss, your care provider may fit you with a custom earmold to reduce feedback
- If you have profound hearing loss, you may be a better fit for a high-powered BTE style hearing aid
- Signia Pure Charge&Go is a prescription device fit and programmed by a professional
- After an initial fitting, you can connect with your care provider remotely through the Signia app
- Signia uses a unique Split Processing technique helps isolate background noise and boost speech clarity
- Signia's Own Voice Processing (OVP) helps take the edge off of that uncomfortable sound quality of the user's own voice that many patients experience when adjusting to hearing aids
- Signia Pure Charge&Go comes in in a small and comfortable receiver-in-canal style that is easy to wear all day
- We prefer Signia's dome tips to other brands for comfort and performance
- Sits behind the ear with a receiver (speaker) that reaches into the ear canal
- Signia Pure Charge&Go is one of the smallest receiver-in-canal hearing aids on the market
- Choose between ten color schemes including: Black, Graphite, Dark Champagne, Silver, Pearl White, Fine Gold, Deep Brown, Sandy Brown, Rose Gold and Beige
- Choose between disposable and rechargeable batteries
- 36+ hours on a full charge
- Popular charger options: Portable charger with induction charging, or plugin Dry & Clean charger
- Signia Pure Charge&Go BCT IX uses Bluetooth Classic to connect with a wide variety of phones and devices
- Signia upgraded their connection strategy in 2025 and is now among the most connected hearing aids in the industry
- Signia Pure Charge&Go is reasonably easy to handle but does require the wearer to place the hearing aid behind their ear and insert the receiver into the ear (consistent across all behind-the-ear styles)
- Signia Pure Charge&Go uses a pin charger with magnets that makes daily charging fairly easy
- Signia Pure Charge&Go is water resistant with an IP rating of 68
- This hearing aid can withstand dust and water submersion in one meter of water for up to 30 minutes
- Signia Assistant: Built in app feature that uses natural language to prompt changes
- Remote care: Included in the Signia app (not a separate app)
- Customization: Treble/bass, volume, microphone directionality, Signia Assistant
- Tinnitus masking: Customizable options through your hearing care professional
- Find my hearing aid: Not available
- Health tracking: Step tracking, activity (e.g., high intensity versus low), and wear time
Phonak Sphere Infinio
- Flagship device from the world’s top hearing aid manufacturer
- Industry-leading onboard AI processing with advanced Spheric mode for enhanced clarity
- Best-in-class Bluetooth streaming, compatible with both Android and iPhone
Phonak’s Infinio and Infinio Sphere models, released in mid-2024, quickly caught industry attention with groundbreaking features:
- Real-Time AI Processing: Phonak leads in AI innovation with its dual-chip architecture, powering real-time adjustments that make listening easier in complex, dynamic environments. This level of AI-driven sound processing sets Infinio Sphere apart as a top choice for clarity and adaptability.
- Extended Bluetooth Range: Enjoy hands-free streaming and calls with 2x the Bluetooth range, making Phonak an ideal pick for both iOS and Android users who value reliable connectivity.
- Waterproof and Durable Design: Built with an IP68 rating, Infinio Sphere withstands water exposure and daily wear, appealing to users with active lifestyles who want durability alongside performance.
Phonak’s Infinio line combines onboard AI with practical, user-focused features, making it an excellent choice for those seeking top-of-the-line performance and versatility in hearing aids.
Phonak Infinio Sphere receives highly positive reviews, with many users noting significant improvements over previous Phonak models and competing brands. Wearers praise its sound quality and robust Bluetooth streaming. The main complaints we found relate to the larger size and occasional automatic mode switching. Some highlights from our partners at ZipHearing.
- "Wearing these new Phonak Sphere Hearing Aids has been very comfortable and an easy adjustment for me. These are my first hearing aids and the sound with them on sounds very natural. I've been able to understand my friends in a crowded restaurant and have been able to turn off the closed captioning on my TV. The Bluetooth feature has worked well for both streaming music and phone calls. I haven't found any drawbacks yet!" - Eileen
- "I have been wearing hearing aids for 6 years. I started my journey with ReSound which lasted nearly 5 years. I then went to Costco and discovered Costco aids are fine for people with modest hearing loss, but I needed more. I then went with Phonak Sphere and have been very happy. I am active and discovered early on the aids I had purchased were being negatively impacted by sweat. Phonak replaced them with water resistant aids for a very small charge. I am very pleased with my new aids." - David
- "Sound quality is excellent. Definitely an improvement over previous HA. Still trying it out in noisy environments but I definitely see an improvement when in noisy situations in understanding speech." - Ken
- "I am currently wearing the Phonak Audio Sphere 90 hearing aids. Had them about two weeks now and the sound quality is very good. I am a bit frustrated with the Automatic program selection as it does not really seem to pick the correct program for the situation. I have not noted the sphere function working as of yet, even though I have been in a few very noisy situations. They are comfortable and only took a few days to adapt to the thicker design of the body. The battery life is exceptional. After wearing them for 15 to 16 hours they still have 45 percent batter life. The only other complaint is the charger case. It is not easy to get they in and almost kink the wires to the domes. I wish they were bigger like my previous Marvels." - Brian
- Top of the line sound processing (thanks in part to onboard AI)
- Best-in-class Bluetooth connection
- Highly water-resistant option available for active lifestyles
- Sphere is a premium product with an average price of $4,598 per pair.
- Shorter than average battery life of 16 hours per charge
- Phonak Sphere is larger than most hearing aids on the market (due to a larger battery and two onboard chips)
- Audéo Infinio (Ultra) Sphere™ is a fully customizable, prescription hearing aid appropriate for mild to severe hearing loss.
- Custom earmolds are often recommended for severe hearing loss to provide superior comfort, improved sound quality, and reduced feedback.
- Audéo Infinio (Ultra) Sphere™ is a prescription device that is fitted and programmed by a Hearing Care Professional (HCP).
- After an initial fitting, you can connect with HCP remotely through the myPhonak app.
- Audéo Infinio (Ultra) Sphere™ provides automatic and precise AI adaptation to surroundings, to reduce listening efforts by separating speech in noisy environments.
- The device uses a first-to-market onboard AI processing chip which makes up to 7 million adjustments per second.
- Infinio Sphere comes in in a comfortable receiver-in-canal style that is easy to wear all day.
- Sits behind the ear with a receiver (speaker) that extends into the ear canal.
- Audéo Infinio Sphere™ offers a rounded, modern form factor and a comparable size to other leading devices.
- Choose from a variety of colors including chestnut, sandalwood, sand beige, silver gray, graphite gray, velvet black, beige, champagne.
- Infinio comes with rechargeable batteries only.
- 24 hours on a 3-hour charge (including 80 min of streaming); 30-minute quick charge provides 6 hours battery life
- The standard charger uses inductive charges.
- Pairs with up to 8 Bluetooth devices, with the flexibility to have 2 simultaneously connected.
- Allows hands-free calling for both Apple iOS® and Android™ devices
- Users can use tap control where they tap their hearing aid to answer and end phone calls.
- Infinio Sphere uses universal connectivity or the Bluetooth Classic Protocol for all Bluetooth devices.
- Infinio Sphere offers 2X the Bluetooth range (distance from your device) compared to older Phonak models.
- Infinio Sphere is designed for ease of use and intuitive handling. Like all behind-the-ear (BTE) styles, it requires the wearer to position the hearing aid comfortably behind the ear and insert the receiver into the ear canal.
- Infinio Sphere devices come with an onboard toggle switch for volume and program changes.
- Infinio Sphere is water resistant with a rating of IP68.
- Infinio Sphere has more robust waterproofing than previous Phonak models. This hearing aid can withstand dust and water submersion in one meter of water for up to 30 minutes.
- Remote care: Available through the Phonak app in coordination with your provider
- Customization: Volume, treble/bass, adjustable custom programs in the app
- Tinnitus masking: Available through your HCP
- Find my hearing aid: Available
- Health tracking: Tracks length of wear time and step count
ReSound Vivia
- ReSound Vivia is a market leader in AI-powered sound processing
- Vivia is one of the smallest RIC hearing aids available
- Auracast-enabled for seamless Bluetooth streaming, developed in collaboration with Bluetooth SIG
- Impressive 20-30 hour battery life on a single charge - even with AI features enabled
- Custom prescription programming provided by a local audiologist
ReSound Vivia is ReSound’s most advanced prescription hearing aid yet—engineered for natural sound, effortless streaming, and top-tier comfort. Here’s what makes it stand out:
- AI-Sound Processing: Vivia features ReSound’s newest 6th-generation chip and a new AI-powered sound management system that helps in loud environments like restaurants or group conversations. Vivia also supports Auracast for future-ready audio streaming in public spaces.
- Design Notes: Vivia is one of the smallest RICs on the market and sits comfortably behind the ear—comfortable even for glasses wearers. It comes in several colors to match hair or skin tone and is built to withstand sweat and water (IP68-rated).
- All-Day Battery Life: Rechargeable models offer up to 30 hours on a single charge and come with a convienient portable charging case. This length of battery life is impressive given the powerful new AI features onboard.
If you’re looking for a small, high-performance hearing aid with cutting-edge AI features, ReSound Vivia is one of the best available today.
Read more reviews via our partners at ZipHearing.
- Noticeable Improvement Over Previous Devices
Many customers say Vivia is a significant upgrade from earlier ReSound models like the Linx Quattro or older analog hearing aids. - Exceptional Sound Clarity
Multiple reviewers highlight Vivia’s ability to deliver natural, nuanced sound and make conversations easier to understand—even in noisy environments. - Great for First-Time or Returning Users
Some users returned to ReSound after years away and found the Vivia to be intuitive, effective, and worth the switch. - Comfortable and Discreet
Wearers appreciate the small size, subtle design, and comfortable fit—even with glasses. - Mixed Feedback on Music and Sound Environments
One reviewer noted that music listening and sound handling in restaurants were still challenging, though they acknowledged the technology may be better suited for different types of hearing loss.
- Great for background noise management
- Auracast compatible
- Small form factor and an optional 3rd microphone in the ear
- 30-hours of battery life
- More expensive compared to direct to consumer and OTC options
- Vivia's in-ear M&RIE microphone is a bit larger and can be uncomfortable for some
- ReSound Vivia is a fully customizable, prescription hearing aid appropriate for individuals with hearing loss in the mild to severe range. Custom earmolds may be recommended for severe hearing loss to provide superior comfort, improved sound quality, and reduced feedback.
- ReSound Vivia combines discreet design with exceptional comfort, making it a good choice for many patients. For those with smaller ear canals, your hearing care professional can easily switch from a M&RIE (Microphone in Receiver) to a standard receiver, ensuring a more comfortable fit without compromising performance.
- ReSound Vivia is a prescription device that is fitted and programmed by a Hearing Care Professional (HCP).
- After initial fitting, you can choose to connect with your HCP remotely through the ReSound app.
- ReSound Vivia is an excellent choice for background noise management. The new onboard AI chip is focused on increasing clarity and the ability to focus on what matters most in challenging listening environments.
- Vivia uses a combination of beam forming microphone technology and noise reduction algorithms to single out speech in complex noise environments.
- ReSound Vivia is a discreet and comfortable hearing aid for most patients. While some patients with smaller ear canals may find the M&RIE uncomfortable in their ears, the M&RIE can easily be changed to the standard receiver by your hearing healthcare provider.
- ReSound Vivia hearing aids fit behind the ear.
- Vivia is among the smallest behind-the-ear devices on the market. Its compact design is especially impressive given the advanced dual-chip architecture and robust battery life, engineered for all-day wear.
- Vivia is offered in a wide range of colors, including new Navy Blue and Red options.
- Vivia is available in three styles, the micro RIE rechargeable, and two disposable battery styles sizes 13 and 312.
- Vivia also offers a CROS (single-sided deafness) compatible rechargeable device.
- Vivia is one of the first hearing aids on the market to release Auracast-compatible hearing aids. Auracast™ allows users to stream public announcements, movies, and other shared audio experiences directly to their hearing aids.
- Vivia also allows standardBluetooth streaming from Apple iOS® and Android™ devices. iPhone users can take calls hands-free. Hands-free mode means that during a call, bi-directional streaming allows the hearing aid user to both hear the call through their hearing aids and use the hearing aid microphones to transmit their voice to the caller.
- Media streaming, however, is one-way only. As long as the phone is compatible, users can stream audio. For FaceTime or Teams calls, streaming is bi-directional.
- Vivia uses Apple's MFI connection and Android's ASHA connection to stream content through Bluetooth.
- Vivia offers a straightforward experience and, like all behind-the-ear styles, simply requires placing the hearing aid comfortably behind the ear and inserting the receiver or custom earmold into the ear.
- Vivia's recharging cases use magnetic charging, which is easier to insert or remove the device from the charger and creates a more consistent charging experience.
- The ReSound Smart 3D app has a feature that uses your phone camera to check that the hearing aids are in the ear properly.
- ReSound Vivia is water resistant with an IP rating of 68
- This hearing aid can withstand dust and water submersion in one meter of water for up to 30 minutes
- Remote care: After an in-office activation and patient accepts the remote care option then remote adjusts could be available between provider and patientvia the app
- Customization: Volume control, treble/bass, streaming treble/bass, programs
- Tinnitus masking: Customizable programs with a hearing care professional or use the Resound Relief app to experiment with masking noise
- Find my hearing aid: This feature is included in the app
- Check my fit: An app feature from Resound to check the hearing aids are in the ear properly
Read our full review of the ReSound App here.
Bonus Options
A few alternatives to consider.
While the products below didn’t make our top picks, they offer unique features or form factors that may be a good fit for certain users.
Apple AirPods Pro 3
- Earbuds and hearing aids in one
- Onboard hearing test via iPhone
- Quality sound in quiet environments
AirPods Pro 3 aren’t just for music anymore—they’re now an FDA-cleared hearing aid alternative built right into Apple’s ecosystem. For users with mild-to-moderate hearing loss, this device offers:
- Built-In Hearing Test: Apple’s custom hearing feature uses a short test to tailor amplification to your needs—no audiologist required.
- Dynamic Sound Enhancement: Speech sounds are emphasized while background noise is reduced, especially in quiet or moderate environments.
- All-in-One Convenience: For iPhone users, AirPods Pro 3 combine assistive listening, media streaming, phone calls, and noise management in one device.
- Many users report meaningful improvements in speech clarity during conversations, especially in quiet settings.
- The onboard amplification is simple to set up and at least somewhat effective for mild hearing loss.
- Users appreciate the seamless experience, with automatic adjustments based on environment and hearing profile.
- Performance is best in quieter spaces—some users note challenges in loud, group environments.
- Built-in hearing test with personalized amplification
- Seamless experience for iPhone users
- Offers hearing aid functionality without a prescription
- Great for phone calls and music
- Less effective in very noisy environments
- Requires some explaination when worn in social settings
- May not be comfortable for all-day wear for every user
Jabra Enhance Select
- Bluetooth enabled and rechargeable
- 100-day risk-free trial
- Nearly invisible with a sleek design
- Professionally programmed before shipping to your home
The Jabra Enhance Select 700 offers an impressive blend of clinic-grade technology, affordability, and user convenience. Here’s why it stands out:
- Professional-Grade Technology at a Lower Price: Jabra’s Enhance Select 700 provides the advanced sound quality of clinic-only brands like ReSound but at less than half the price.
- Professional Programmed Hearing Aids From Home: Jabra’s pre-programmed approach ensures a personalized fit without needing in-clinic visits—customers simply take or upload a hearing test, and Jabra's audiologists program the hearing aids before shipment.
- Seamless Bluetooth Streaming: Equipped with LE Audio, the Enhance Select 700 delivers high-quality, direct streaming for calls and media, with excellent sound quality and range.
- Purchase Perks: Jabra offers 100-day returns, unlimited remote adjustments, and seven-day-a-week customer support.
Overall
Users commend the Jabra Enhance Select 700 for its natural sound quality, discreet design, and effective customer support. Many report significant improvements in hearing clarity and comfort.
Positives
- Natural Sound Quality: "The sound quality is excellent, and the ability to adjust settings via the app is a great feature." — Timothy T.
- Discreet Design: "These hearing aids are virtually invisible and very comfortable to wear throughout the day." — Angel M.
- Customer Support: "The customer service team was incredibly helpful and guided me through the setup process with ease." — Damian.
Complaints
While the majority of feedback is positive, some customers have reported issues with device durability and the need for adjustments. However, these concerns are relatively infrequent compared to the overall satisfaction expressed by users.
For a comprehensive view of customer experiences, you can visit Jabra Enhance's review page.
- One of the most affordable and convenient ways to purchase online while maintaining professional care
- Comes with a 100 day free-return period
- Offers rechargeable batteries and Bluetooth streaming
- Remote care requires users to be somewhat tech savvy
- Jabra only offers styles that sit behind the ear
- Jabra Enhance Select is a fully customizable, prescription hearing aid appropriate for mild-severe hearing loss
- If you have severe hearing loss and struggle with feedback (squealing) you may need a custom earmold (not available through Jabra Telehealth)
- If you have profound hearing loss, you may be a better fit for a high-powered BTE style hearing aid (note available through Jabra Telehealth)
- Jabra is a remote care brand that programs and delivers your hearing aids through Telehealth
- Take or submit a hearing test and a Jabra professional will program your hearing aids and ship them to your door
- Three years of unlimited support is included with every purchase
- Jabra Enhance Select hearing aids come with the capability for remote adjustments. This feature means you don't need to ship your hearing aids back to get program updates
- Jabra Enhance Select is manufactured by GN Hearing (the makers of ReSound hearing aids)
- Jabra devices come with a strong set of background noise handling features and app controls
- Jabra Enhance Select comes in a small and comfortable receiver-in-canal style that is easy to wear all day
- Sits behind the ear with a receiver (speaker) that reaches into the ear canal
- The form factor of Jabra Enhance Select is comparable to ReSound hearing aids
- Choose between five colors including: Sparkling Silver, Champaign, Gold, Bronze and Warm Grey
- Jabra Enhance Select offers three levels of technology. Select 500 and Select 300 come with rechargeable batteries and as of May 2024, Select 50 also comes with rechargeable batteries
- 30 hours on a full charge
- Comes with a portable charger (does not need to be plugged in)
- All Jabra Enhance Select technology levels allow Bluetooth streaming, music listening, and phone calls.
- Jabra Enhance Select 500 uses Bluetooth LE Audio (Auracast ready) and is handsfree for iPhone (11 and newer) and compatible Android models
- Jabra Enhance Select 300 allows iPhone users to take calls hands-free, while Android users must keep their phones close to pick up outbound audio
- Jabra Enhance Select 300 uses Apple's MFI connection and Android's ASHA connection to stream content through Bluetooth
- Jabra Enhance Select is reasonably easy to handle but does require the wearer to place the hearing aid behind their ear and insert the receiver into the ear (consistent across all behind-the-ear styles)
- If dexterity is a concern we recommend Select 300, which is larger and easier to grasp than the microRIE (Select 500)
- The Jabra Enhance Select charge case uses induction charging and is fairly easy to handle
- All levels of Jabra Enhance Select have an IP rating of 68
- These hearing aids can withstand dust and water submersion in one meter of water for up to 30 minutes
- Customization: Treble/bass, volume, microphone directionality
- Jabra Enhance Select includes Telehealth capabilities through the Jabra app
Eargo 8
- Disruptive leader in hearing health, known for sleek, invisible design.
- Rechargeable with a patented ear tip that allows ears to breathe.
- Eargo 8 adapts to your environment automatically throughout the day.
- Budget models (Eargo SE and Eargo LINK) offer lower prices and alternate features.
Eargo has long set the standard for invisible-style design in the hearing aid industry. Their compact devices, along with an intuitive app and thoughtful packaging, make Eargo a standout choice for early adopters. Here’s why we picked it:
- Invisible Design: The Eargo 8 is one of the smallest rechargeable hearing aids on the market, rivaled only by the Sony CRE-C20.
- Reduced Occlusion: Eargo’s patented “floating” ear tip design sits comfortably in the ear without causing occlusion, a common issue for in-ear hearing aid users.
- User-Friendly App: The Eargo app is easy to navigate, and it allows audiologists to remotely adjust your devices as needed, though most adjustments can be managed directly in the app.
Eargo has received numerous customer reviews, reflecting a generally positive reception.
Overall
Customers frequently commend Eargo for its discreet design, sound quality, and responsive customer service. Many users highlight the significant improvement in their hearing experience and the comfort of the devices.
Positives
- Discreet Design: "The Eargo hearing aids are virtually invisible, and no one can tell I'm wearing them." — James D.
- Sound Quality: "The clarity of sound is remarkable; I can hear conversations clearly even in noisy environments." — Charlie B.
- Customer Service: "Eargo's support team was incredibly helpful and guided me through the setup process with ease." — Rowdy G.
Complaints
While the majority of feedback is positive, some customers have reported issues with device durability and the need for adjustments. However, these concerns are relatively infrequent compared to the overall satisfaction expressed by users.
For a comprehensive view of customer experiences, you can visit Eargo's review page.
- Eargo is a tiny, rechargeable device that sits entirely inside the ear
- Eargo uses a unique design that prevents occlusion
- Eargo is self-fit using an app but offers remote support
- Only appropriate for those with mild to moderate hearing loss
- Requires some tinkering to fine tune the product
- Eargo is not Bluetooth enabled due to the tiny size
- Eargo 8 hearing aids are sold over the counter and are appropriate for those with mild-moderate hearing loss
- If you have more significant hearing loss it is recommended that you access professional care through Telehealth or local care
- Available for purchase online or at retail stores like Verizon Victra and Best Buy
- Does not require a prescription from a doctor
- Customize your hearing aids with an onboard hearing test and app-controls
- Eargo has well-developed background noise management algorithms
- Smart Sound Adjust automatically adapts to your environment and focuses on voices
- Eargo sits inside of the ear and is one of the most comfortable in-ear options on the market
- Eargo creates less occlusion than many in-the-ear options
- Our team finds all in-the-ear models slightly less comfortable than RIC hearing aids
- Sit inside the ear
- Only available in one completely-in-canal size (nearly invisible in many ears)
- Only available in black
- Eargo hearing aids are rechargeable
- 16 hours of battery life on a single charge
- Each pair of hearing aids comes with a small and portable recharge case that carries 14 additional charges
- Eargo 8 does not offer Bluetooth streaming
- Eargo 8 is small but comes with rechargeable batteries which prevents difficult battery changes
- Eargo's devices include a pull-tab that makes it easier to place and remove the devices in your ears
- Eargo 8 hearing aids have an IP68 rating, meaning they can be submerged in up to one meter of water for 30 minutes without damage.
- Eargo 8 pairs with a smartphone app that includes an onboard hearing test and manual controls for programs, volume, and sound quality.
- You can also adjust volume and switch programs without the app by simply double-tapping your ear.

If we could sit down with each reader to help them find the perfect hearing aid, these are the steps we would follow.
Step 1: Understand Your Hearing Loss
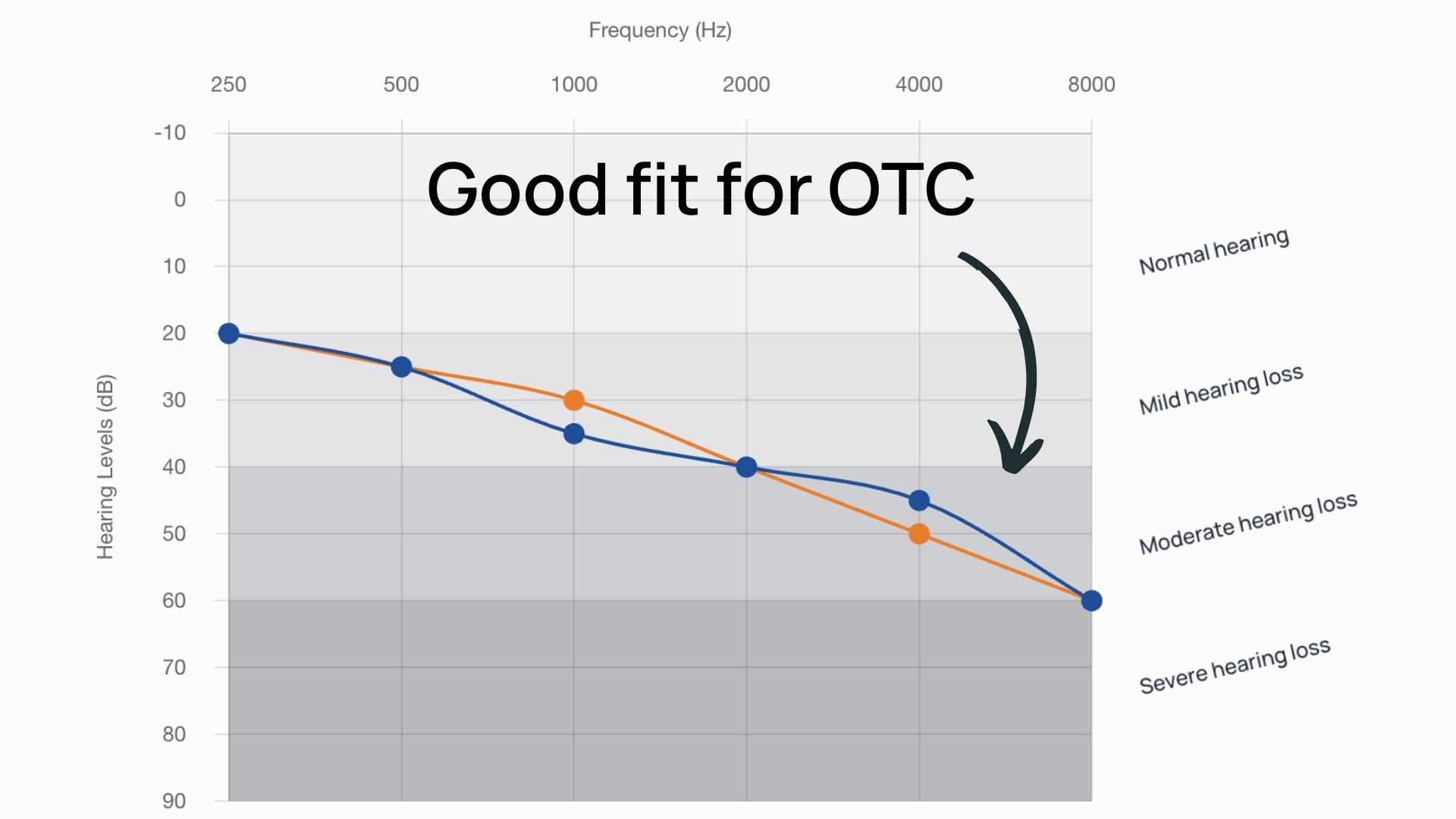
The first and most crucial step in choosing a hearing aid is understanding your individual hearing loss. You can do this at a local clinic or by taking our online hearing test. There are two key factors you need to know about your hearing loss: its severity and its shape.
Severity of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is typically categorized as mild, moderate, severe, or profound. In some cases, you might have mild hearing loss in certain frequencies and moderate loss in others, which is often referred to as mild-moderate hearing loss.
Why does this matter? OTC and telehealth hearing aids (like Sennheiser and Eargo listed above) are generally best suited for mild to moderate hearing loss. If you have severe or profound hearing loss, the "best" hearing aid for you will likely come from the locally prescribed category, as these devices can be better customized to meet more complex needs.
Shape of Hearing Loss
The shape of your hearing loss is another important factor. The most common type of hearing loss follows a downward slope from left to right on an audiogram, meaning your ability to hear higher frequencies is more affected than lower ones. If your hearing loss resembles this pattern, you're in the majority and could be a good candidate for self-fitting options.
However, if your hearing loss varies significantly between ears or has a less typical shape—like a reverse slope, where high frequencies are better than low frequencies—consulting with our team or visiting a local clinic is the best path forward.
Still wrapping your head around your hearing test results? Check out our full video on the topic below. 👇
Step 2: Choose a Care Method
Once you understand your hearing loss, the next step is to decide on the best care model.
Telehealth and OTC options are often more convenient and can cost anywhere from 25% to 100% less than traditional in-clinic care. These care models rely on you being comfortable using a smartphone and setting up the devices yourself, so if you're someone who prefers face-to-face support or needs assistance with the setup, a locally prescribed option might be the better choice.
That said, most people adapt well to telehealth and OTC models, especially with the support offered through Soundly. See our full video comparing RX Vs. OTC hearing aids below.
Step 3: Select Features and Styles
Finally, you’ll want to think about the style of hearing aid and the features that are most important to you. Here’s a quick breakdown:
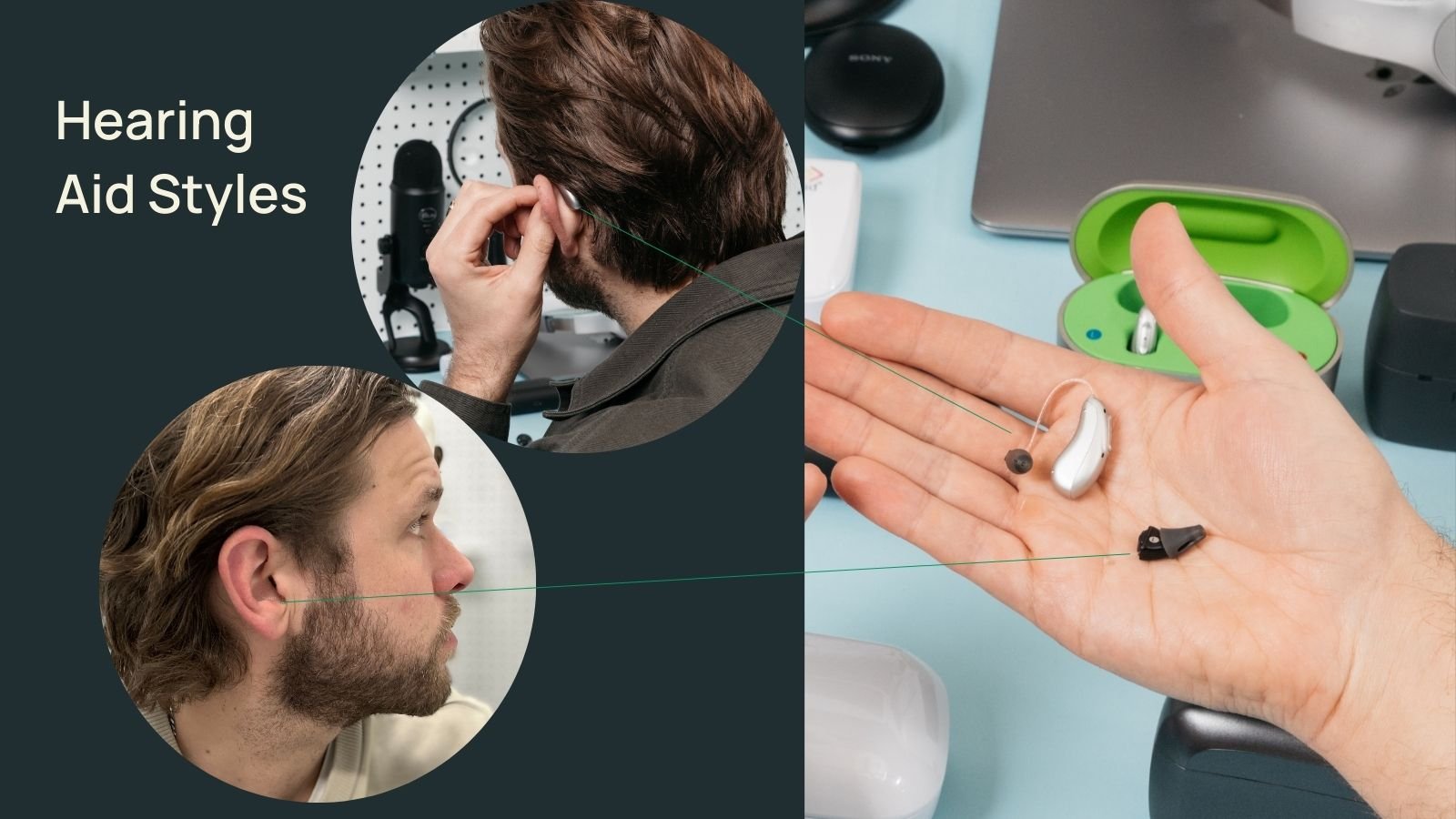
Styles
- In-ear: These are often easier to handle (especially models like the Eargo 8) with rechargeable batteries). However, in-ear hearing aids may not always include Bluetooth streaming.
- Behind-the-ear (BTE): This style typically includes Bluetooth streaming and offers more space for microphones, which can improve sound processing. About 80% of hearing aid wearers choose behind-the-ear models, but there are good reasons to consider both styles.

Key Features to Consider
- Bluetooth: Allows for streaming audio directly from your smartphone.
- Rechargeable batteries: No more fiddling with small batteries—just plug in at night.
- Smartphone app controls: Adjust settings like volume, EQ, or even customize how your hearing aids respond in different environments.
- Tinnitus masking: Some hearing aids can play white noise to help mask tinnitus.
- Step tracking: Certain models track your daily steps for added health insights.
- Waterproofing: Most hearing aids on this list are water-resistant to some degree, which is great for daily use and sweat protection.
Hearing Aid Shopping Advice for Caregivers
If you’re researching hearing aids for someone else, there are a few additional factors to consider to make sure the device suits both their needs and yours as a caretaker.
- Easy Setup and Maintenance: You may want a device that’s simple to set up on your phone and continues to function seamlessly, even after you leave. The Sennheiser All Day Clear is particularly well-suited for this scenario. It’s comfortable, rechargeable (which is helpful for those with dexterity issues), and features an intuitive setup process.
- One of the standout features of Sennheiser’s device is the onboard hearing test. Instead of responding to beeps or using external sounds like a TV to test the hearing aids, the wearer simply listens to a conversation between two people. They select the version of the conversation that sounds the clearest to them, which makes the process more user-friendly for those who might struggle with more traditional methods of hearing testing.
- Reputable Brands with Simple Interfaces: The most important factor for caretakers is choosing a hearing aid from a trusted brand with a straightforward interface. You want a device that’s reliable and won’t require constant troubleshooting, making your role as a caretaker easier.
- In-Person Care: For individuals who may have more complex needs or require additional assistance, you might opt for in-person care at a local audiology clinic. While it may require transportation, having face-to-face support can be invaluable for ensuring the hearing aids are correctly fitted and properly maintained.
By keeping these factors in mind, you’ll be able to choose a product that works well for both the wearer and you as a caretaker.
What You Need to Know About Hearing Aid Prices
Hearing aid prices vary widely depending on the type of hearing aid and care model. Prices typically range from around $500 to $6,500 per pair, with over-the-counter (OTC) devices generally costing less (closer to the lower end) and prescription hearing aids at the higher end.
- Over-the-Counter (OTC) hearing aids: These are typically available for $500 to $2,000 per pair and do not require a prescription. OTC hearing aids are best suited for those with mild to moderate hearing loss and those comfortable with self-fitting via a smartphone app.
- Telehealth or remote programming hearing aids: These options offer professional programming but at a more affordable cost compared to in-clinic models. Prices generally start at $1,500 per pair and go up depending on the features included.
- Prescription hearing aids: These are often more expensive, ranging from $3,000 to $6,500 per pair. This cost includes the in-person fitting, testing, and ongoing support from a licensed audiologist.
Striking a Balance on Price
Based on our experience, $900 / pair seems to be the threshold for devices that deliver good sound quality and long-term reliability. Products for just a few hundred dollars generally don’t perform well in our real-world tests or break down more quickly.
Hearing Aids and Insurance
Most insurance plans do not cover hearing aids, though some states require certain insurance policies to offer hearing aid coverage for children, and Medicare does not cover hearing aids. However, some Medicare Advantage plans (Part C) and private insurers may provide limited coverage for hearing aids and hearing exams. Veterans may also be eligible for hearing aids through the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), depending on their level of service and hearing loss.
It's important to check with your insurance provider to understand what coverage, if any, is available. Some providers offer reimbursement for hearing tests, fittings, or a portion of the device cost, but these benefits vary widely.
For those paying out of pocket, financing plans and payment programs are often available through hearing aid manufacturers or retailers, allowing you to spread the cost over several months or years. Additionally, flexible spending accounts (FSA) or health savings accounts (HSA) can be used to cover hearing aid costs, which can help reduce the financial burden.
Best Hearing Aids on the Market - Final Thoughts
We’ve covered a lot of ground in this guide, from understanding the different hearing aid styles and care models to finding the right balance of sound quality, comfort, and price. Whether you’re just beginning your journey or are ready to replace an old pair of hearing aids, we hope this guide has given you the clarity and confidence to move forward.
At Soundly, we’ve had the privilege of helping millions of people navigate these decisions, and we’re here to support you every step of the way. If you still have questions or need more personalized guidance, feel free to take our hearing test to get a tailored recommendation based on your hearing needs.
And if you’d rather chat with us directly, we’d love to hear from you! Just send us an email at [email protected], and we’ll be happy to help you on your journey to better hearing.
You don’t have to navigate this process alone—let us help you find the best solution for your unique needs!
Frequently asked questions
If you often turn up the TV volume, ask others to repeat themselves, or struggle to hear a partner in the other room, these may be signs of hearing loss. A quick way to check is by taking an online hearing test, which can help determine if hearing aids might be beneficial for you.
Hearing aids typically last 3 to 5 years. With proper care, including regular cleaning and parts replacement, some last up to 6 or 7 years. However, many users upgrade around the 3-year mark due to improvements in technology.
Yes. Since tinnitus is often linked to hearing loss, all hearing aids can help by restoring sound input. Some models also include dedicated tinnitus masking features, which play white noise at various frequencies. The Elehear Beyond is an OTC option with tinnitus support, while Widex specializes in tinnitus relief in the prescription category.
Most modern hearing aids use rechargeable batteries that last 20 to 40 hours per charge. While disposable batteries offer flexibility, rechargeable options are more common, convenient, and future-proof. Built-in batteries typically last at least 3 years, and most manufacturers offer warranties on battery performance.
Yes. Nearly all hearing aids connect to a smartphone app for control, which works on both iPhones and Android devices. For streaming, compatibility varies—Sonova products like the Sennheiser All Day Clear and Phonak Infineo are particularly strong with Android, while most other brands optimize for iPhone.
Yes. Hearing aids with an IP68 rating can withstand submersion in up to one meter of water for 30 minutes. Most hearing aids in our Best-of guide meet this standard and are resistant to splashes or accidental exposure to water. Check out our Soundly Scorecard for each product to see its level of water resistance.
Insurance rarely provides full coverage for hearing aids but may offer discounts through specific retailers or networks. Check with your provider for details, and see our full insurance guide for more information. See our full guide to the topic of insurance here.
Yes. Hearing aids are eligible for HSA and FSA purchases. You can use your HSA or FSA card here at Soundly.com or call us for assistance.
Yes. Most hearing aids offer a trial period. At Soundly, customers get 45 to 100 days depending on the product. Prescription clinics typically offer 45-day trials. If a brand doesn’t provide a trial period, we recommend avoiding it.